Why is Zero Trust Becoming so Important?
Jul 01, 2021
iCrowdMarketing powered by iCrowdNewswire
 To say that the cybersecurity industry has gone through a very tedious couple of years is a phenomenal understatement. Cybersecurity, or in short digital defense tools and knowledge (antiviruses, antimalware, firewalls et al.), protects systems and networks. According to industry giant Microsoft, they go into quite a bit of detail on this; “Today’s organizations need a new security model that more effectively adapts to the complexity of the modern environment, embraces the mobile workforce, and protects people, devices, apps, and data wherever they’re located.” Furthermore, “Instead of assuming everything behind the corporate firewall is safe, the Zero Trust model assumes breach and verifies each request as though it originates from an open network. Regardless of where the request originates or what resource it accesses, Zero Trust teaches us to “never trust, always verify.” Every access request is fully authenticated, authorized, and encrypted before granting access. Microsegmentation and least privileged access principles are applied to minimize lateral movement. Rich intelligence and analytics are utilized to detect and respond to anomalies in real-time.” Those of us that live online and have done so for years, especially anyone working in the IT industry knows why cybersecurity is ‘numero uno’ right now. Zero-Trust is not just more techno-babble, oh no, not at all. It is at the top of the mountain of the most significant paradigms/strategies that will be invaluable for the battle against global cybercrime.
To say that the cybersecurity industry has gone through a very tedious couple of years is a phenomenal understatement. Cybersecurity, or in short digital defense tools and knowledge (antiviruses, antimalware, firewalls et al.), protects systems and networks. According to industry giant Microsoft, they go into quite a bit of detail on this; “Today’s organizations need a new security model that more effectively adapts to the complexity of the modern environment, embraces the mobile workforce, and protects people, devices, apps, and data wherever they’re located.” Furthermore, “Instead of assuming everything behind the corporate firewall is safe, the Zero Trust model assumes breach and verifies each request as though it originates from an open network. Regardless of where the request originates or what resource it accesses, Zero Trust teaches us to “never trust, always verify.” Every access request is fully authenticated, authorized, and encrypted before granting access. Microsegmentation and least privileged access principles are applied to minimize lateral movement. Rich intelligence and analytics are utilized to detect and respond to anomalies in real-time.” Those of us that live online and have done so for years, especially anyone working in the IT industry knows why cybersecurity is ‘numero uno’ right now. Zero-Trust is not just more techno-babble, oh no, not at all. It is at the top of the mountain of the most significant paradigms/strategies that will be invaluable for the battle against global cybercrime.Zero-Trust came around in 2010 when weaknesses in traditional security models were being discussed by research organizations. The traditional model assumed trust for every device within the network, which is the classic perimeter system, but researchers saw very obvious loopholes in this existing method and requested immediate attention. In fact, in 2018 statistics reveal that interest in Zero-Trust started booming. Why the need for all the hype around new security models in the industry? Well, this is because traditional cybersecurity that is perimeter-based (a classic model in use for decades) is becoming obsolete. Classic systems are having great difficulty keeping up with new digital complexities such as; modern developer environments, hybrid work models, and dynamic endpoints. The digital transformation that is already well established, with thousands of organizations already running in full digital, there is an onslaught of billions of IoT devices (Internet of Things) that are nowhere near sufficiently protected.
What is Cybercrime?
Cybercrime is, in short, crime in the digital realm (which takes place on the internet caused by digital/cybercriminals.) Cybercrime comes in many shapes and sizes e.g. from the top of the chain which is ransomware to elementary level frauding and scamming via phishing. According to Avast on what cybercriminals do “Cybercriminals buy and sell malware online (generally on the dark web) while also trading in services that test how robust a virus is, business intelligence dashboards to track malware deployment, and tech support (that’s right — crooks can contact a criminal helpline to troubleshoot their illegal hacking server or other malfeasance!). The professionalization and proliferation of cybercrime add up to countless costs in damages every year, impacting individuals, businesses, and even governments. Experts estimate that cybercrime damages will reach $6 trillion annually by 2021, making it one of the most lucrative criminal enterprises.”
Is Zero-Trust The Future of Cybersecure Organizations?
There are several reasons for implementing Zero-Trust solutions, albeit they are not easy to add to an organization’s infrastructure, and will undoubtedly cause several impracticalities. Nevertheless, Zero-Trust implementation is looking like it’s going to be unavoidable because organizations need a new security model for new times. A new model of cybersecurity that can adapt to new complexities, is capable of protecting the mobile and remote workforce as well as the countless devices, data, and apps located in millions of locations. First, let’s look at the advantages of Zero-Trust;
- Heightened mobile security (remote devices)
- Helps with digital transformation and secure transition to the cloud
- Better adapted cybersecurity for gaps in security and lateral movement of malware
- Constant authentication, authorization on all data points
- JIT/JEA user access profiles
- Security built-in from the ground up
- Real-time monitoring and security management
- Multi-factor authentication
Zero-Trust is a very strict security paradigm, that as we have covered above will be unavoidable in the future. The Zero-Trust model immediately assumes the worst scenario and asks for authorization and verification on every access layer. This is why it is referred to as a ‘never trust, always verify’ model. Every time a layer is accessed with a Zero-Trust model in place, data transmission, keys, and credentials are authenticated, authorized, and finally encrypted before any access is granted. Below is a Zero-Trust model security diagram from an organizational strategic point of view.
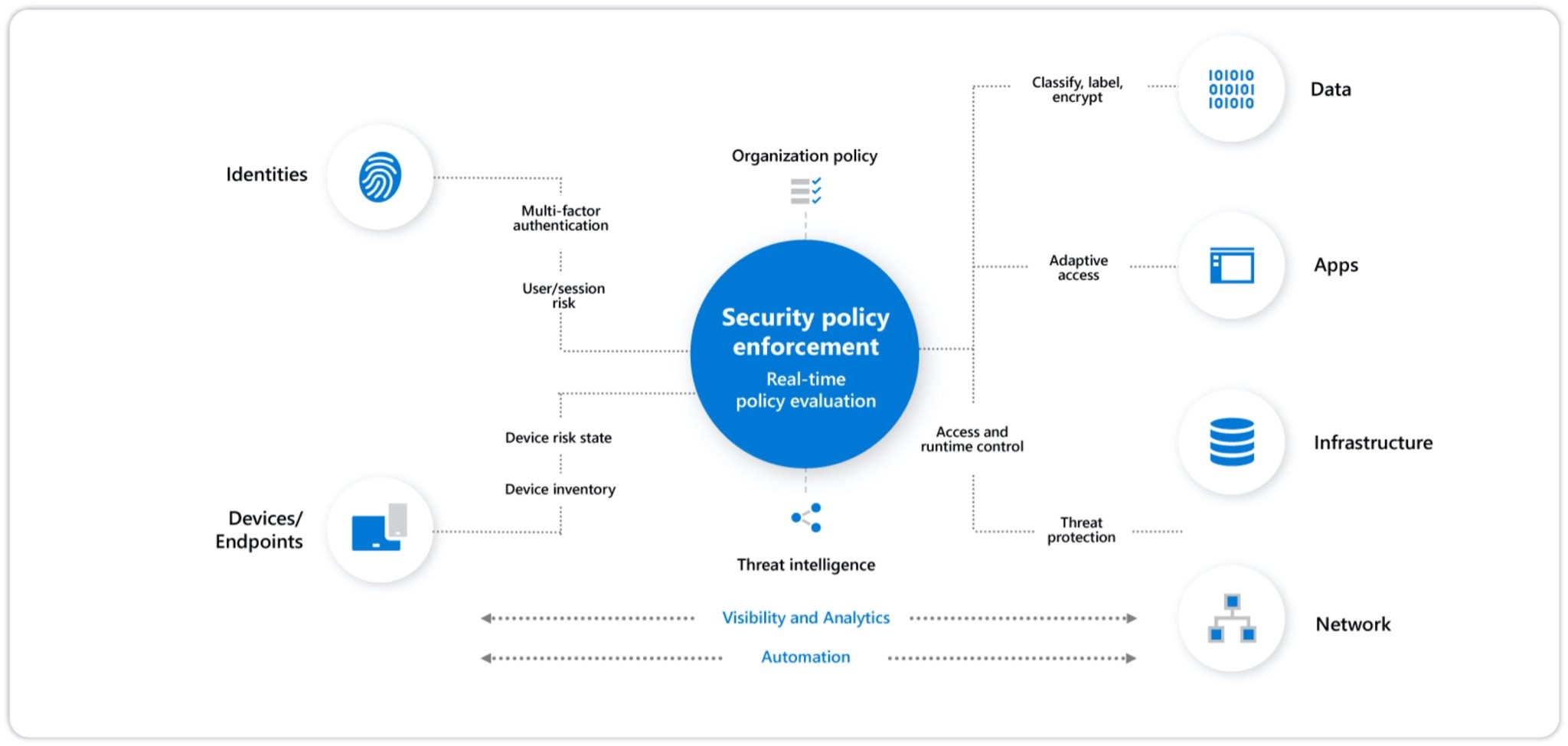
The Zero-Trust model intrinsically does not trust anyone- even those within the network. This implies constant monitoring and management. So, we’ve covered some advantages and a broader view of Zero-Trust, but what about the problems, disadvantages, and challenges?;
- The complexity of setting up such a model due to reorganization of policies in transition
- The need to educate users for a good familiarity with Zero-Trust models
- Potential incompatibility with legacy (older and obsolete) systems
- Increased requirement for an increased amount of users and levels of access
- More devices that are required to be managed means tailored access
- Data configuration difficulties due to multiple storage locations and the cloud
Zero-Trust: Remedy or Hindrance?
Thankfully most of the disadvantages or cons related to Zero-Trust are to do with the effort and work required to implement it. Metaphorically speaking, Zero-Trust is like implementing a trained autopilot to start driving your car for you, better than you can and with quicker reactions. Of course, this means that the solution is going to cost and take time to implement. Some businesses may not see that the benefits outweigh the costs, but objectively it is an excellent, sophisticated security model and a natural evolution to classic perimeter-based security. A world without Zero-Trust will not be a safe world in the future, with cybercrime now causing cyber-physical damage and infiltrating the toughest security walls of any establishment. With a Zero-Trust model in place, once it is budgeted in and personnel is allotted for this, it doesn’t mean that an organization can’t be breached. The trick is that, even if there is a breach, the malicious software cannot move any further in any direction and continue to affect other devices in the network thanks to Zero-Trust.
Tags: English